The pressing imperative to tackle climate change and diminish greenhouse gas emissions has spurred a surge in decarbonization initiatives throughout diverse sectors of the global economy. Decarbonization entails shifting from carbon-intensive practices to adopting low or zero-carbon alternatives in industries, transportation, and buildings. This article delves into the essence of decarbonization and its profound impact on these sectors, as they strive to mitigate climate change and forge a sustainable future. By exploring the concept of decarbonization, we gain insights into the transformative measures being undertaken to combat climate change and pave the way for a more sustainable tomorrow.
Understanding Decarbonization
Decarbonization refers to the process of reducing or eliminating carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gas emissions from human activities. The power generation, industry, transport, buildings, and agriculture sectors are major contributors to global emissions [1]. To mitigate the impacts of climate change, these sectors must undergo significant transformations.
Decarbonizing Power Generation
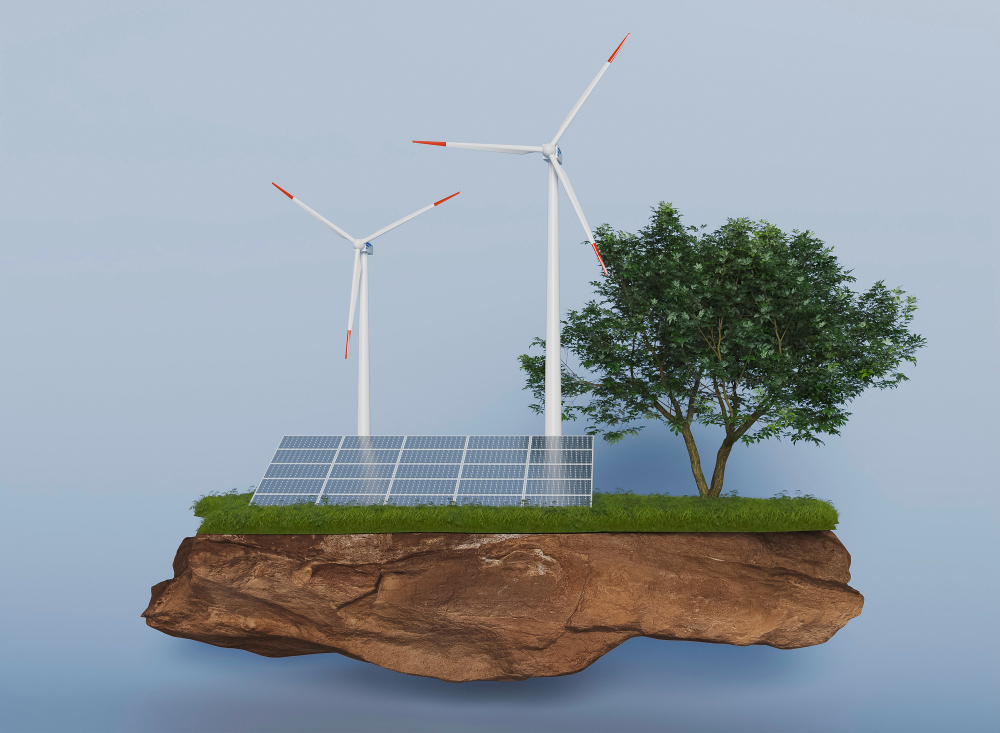
The power generation sector plays a crucial role in decarbonization efforts. Transitioning from fossil fuel-based power sources to renewable energy is key to reducing emissions. Renewable energy sources like solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal power offer clean alternatives that can replace coal-fired power plants and reduce CO2 emissions [1]. Additionally, grid modernization and energy storage technologies enable better integration of renewable energy into the power grid, ensuring a stable and reliable energy supply [1].
Decarbonizing Industry
Industries are significant contributors to carbon emissions, but decarbonization strategies are being developed to mitigate their environmental impact. Clean technologies and process optimization help reduce energy consumption and emissions in manufacturing processes. The concept of a circular economy, which focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency, plays a vital role in decarbonizing industries [2].
Decarbonizing Transport
The transport sector is a major source of carbon emissions, and decarbonizing it is crucial for achieving sustainability goals. Electrification of vehicles, including cars, buses, and trucks, is gaining momentum as a key strategy to reduce transport emissions. The shift from internal combustion engines to electric vehicles (EVs) decreases reliance on fossil fuels and contributes to lower emissions [3]. Investing in public transportation systems and promoting shared mobility options such as ride-sharing and bike-sharing further helps reduce the carbon footprint of transportation. Moreover, developing the necessary charging infrastructure and supporting policies are essential for accelerating the adoption of EVs [3].
Decarbonizing Buildings
Buildings account for a significant portion of energy consumption and emissions. Decarbonizing the building sector involves designing and constructing energy-efficient buildings that minimize energy demand. Incorporating sustainable materials, efficient insulation, and advanced HVAC systems can significantly reduce energy consumption. Retrofitting existing buildings with energy-saving measures and implementing effective energy management practices further contribute to decarbonization efforts [1].
Challenges in Decarbonization
While decarbonization is crucial, it faces several challenges. Many developed countries still rely on high-carbon infrastructures and lifestyles, which pose obstacles to rapid decarbonization [3]. Technological and financial barriers need to be overcome to facilitate the widespread adoption of low-carbon alternatives. Furthermore, effective policy and regulatory frameworks are essential to drive the necessary transformations and incentivize sustainable practices across industries, transport, and buildings.
The Economic Benefits of Decarbonization
Decarbonization is not only vital for environmental sustainability but also offers significant economic benefits. Studies suggest that a low-carbon economy can yield gains of about $26 trillion by 2030 [2]. Decarbonization efforts create new job opportunities and foster innovation in clean technologies and sustainable practices, driving economic growth and competitiveness in the long run.












0 Comments