Indian cinema, lovingly known as Bollywood, boasts a captivating and dynamic history that extends back more than a century. From its modest origins during the era of silent films to its present status as a global cultural phenomenon, Indian cinema has undergone a remarkable transformation, mirroring the socio-cultural tapestry of the nation. In this article, we embark on an enthralling expedition through the realms of Indian cinema, uncovering its significant milestones, iconic films, visionary filmmakers, and the profound influence it has wielded over popular culture.
Table of Contents
- I. Introduction
- II. The Silent Era: Birth of Indian Cinema
- III. The Golden Age: Indian Cinema Comes of Age
- IV. Regional Cinema: Diverse Narratives and Cultural Influences
- V. The New Wave: Indian Cinema Reimagined
- VI. Bollywood: The Cultural Phenomenon
- VII. Technological Advancements and Changing Landscape
I. Introduction
Indian cinema holds immense cultural and historical significance. It is a powerful medium that has not only entertained millions but also played a crucial role in shaping the collective identity of the Indian people. Understanding the history of Indian cinema provides insights into its evolution and its impact on society.
II. The Silent Era: Birth of Indian Cinema
The arrival of cinema in India can be traced back to the Lumière Brothers’ screenings in 1896. Indian filmmakers quickly embraced the medium, with Dadasaheb Phalke’s “Raja Harishchandra” (1913) marking the birth of Indian feature films. Pioneering filmmakers like Himanshu Rai, Franz Osten, and Bombay Talkies contributed to the growth of Indian cinema during this era.
III. The Golden Age: Indian Cinema Comes of Age
The advent of sound in the 1930s brought a new era of storytelling in Indian cinema. Social and political events, such as India’s struggle for independence, influenced the themes and narratives of films. The golden age saw the emergence of legendary actors like Raj Kapoor, Dilip Kumar, and actresses like Nargis and Madhubala. Filmmakers like Guru Dutt, Bimal Roy, and Satyajit Ray created masterpieces that are considered classics of Indian cinema.
IV. Regional Cinema: Diverse Narratives and Cultural Influences
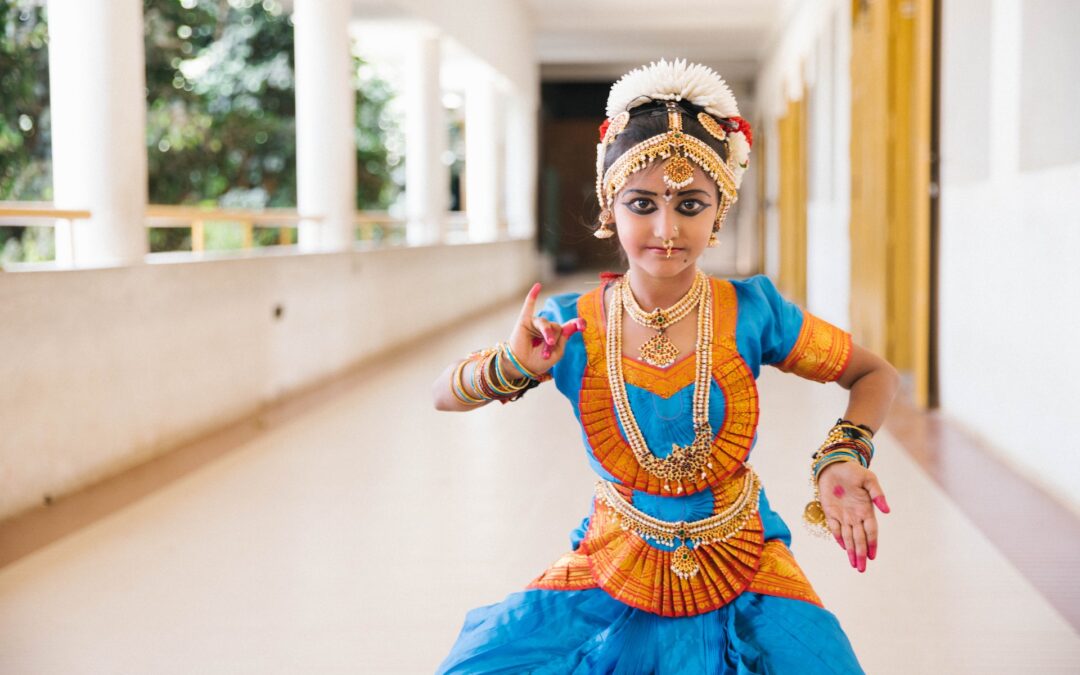
Indian cinema is not limited to Bollywood alone. Regional film industries, such as Tamil, Telugu, Bengali, and Malayalam cinema, have made significant contributions to the Indian film heritage. These industries have their own distinct styles, narratives, and cinematic traditions. Iconic films and filmmakers from different regions have showcased the diversity and cultural richness of India.
V. The New Wave: Indian Cinema Reimagined
In the 1950s and 1960s, a parallel cinema movement emerged, challenging the conventions of mainstream Indian cinema. Filmmakers like Satyajit Ray, Mrinal Sen, and Shyam Benegal ushered in a new wave of artistic experimentation and realism. Indian cinema also underwent transformation due to globalization, with filmmakers exploring contemporary themes and incorporating international influences.
VI. Bollywood: The Cultural Phenomenon
Bollywood, the Hindi film industry based in Mumbai, has played a significant role in popularizing Indian cinema globally. Known for its extravagant song and dance sequences, melodrama, and larger-than-life narratives, Bollywood has captivated audiences not just in India but also across the world. Bollywood films and stars have become cultural ambassadors, influencing fashion, music, and popular culture trends.
VII. Technological Advancements and Changing Landscape
Indian cinema has witnessed significant technological advancements over the years. The introduction of color, widescreen formats, and digital technology revolutionized the visual experience for audiences. The use of special effects and CGI has enhanced storytelling possibilities, enabling filmmakers to create spectacular and immersive cinematic experiences. Streaming platforms have further transformed the distribution and consumption of films, bringing Indian cinema to a global audience.












0 Comments